“At present, 7.7 crore people are suffering from diabetes. After the pandemic, type-2 and type-1 diabetes are being seen not only in cities but also in villages. This is a huge cause of concern for doctors everywhere,” says Dr Kalra, a renowned endocrinologist and the former President of the Endocrine Society of India.
The most common myth about diabetes in India or other parts of the world is that it is a disease. It is a genetic disease that has no cure. But maintaining precautions is a must.
But no, this is not true. It can be cured most easily by consulting a doctor, or the simplest way is through home remedies, which might take some time to cure, but the outcomes are perhaps slow.
Some people don’t even consider preferring medical treatments because they think controlling sugar levels or not eating specific foods is the cure for all.
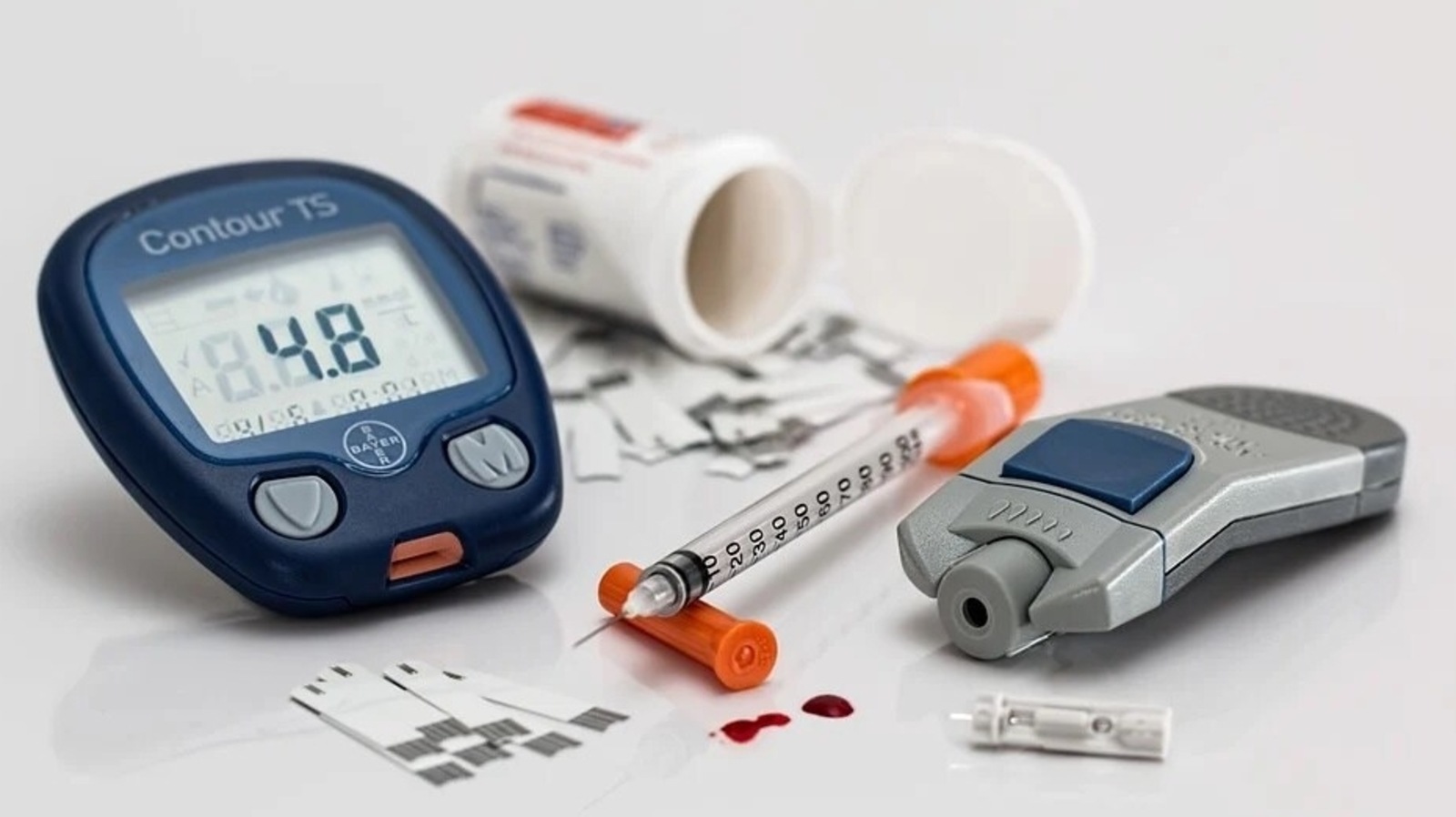
That’s how their complications become problematic with time.
Several myths about diabetes that exist are all too common and have been reported, by which misrepresentations of diabetes can be harmful and lead to an unfair stigma around the situation.
Myth 1
Eating no sugar is the only way to cure diabetes.
The truth: People with diabetes need to eat a balanced diet that can include some sugar in moderation. That means diabetic people can eat sugar.
Myth 2:
Type 2 diabetes is mild.
The Truth: No form of diabetes is mild.
If type 2 diabetes is poorly managed, it can lead to serious (even life-threatening) complications.
Myth 3:
Type 2 diabetes only affects fat people.
The truth: Around 20% of people with type 2 diabetes are of normal weight or underweight.
Myth 4:
Diabetics will only consume adiabatic foods.
The truth: Diabetic food will often still affect blood glucose levels, be expensive, and may also cause adverse side effects.
Myth 5:
Diabetes can affect, taking away eyesight and losing a person’s legs.
The truth: Blindness and amputation are preventable, and the vast majority of people with diabetes will avoid blindness and amputation, particularly if annual diabetic health checks are conducted each year.
These myths have been a common perception in India towards diabetes.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a problematic health challenge globally. It is a metabolic disease characterized by a high level of glucose in the body due to the inability of the pancreas to produce or use adequate insulin.
Understanding of how debates are classified
There are three types of diabetes:
Type 1
Diabetes, wherein the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells.
Type 2
Diabetes mellitus is a type of diabetes where the human body does not produce adequate insulin or develops resistance to it, and gestational diabetes is detected during pregnancy and can cause complications for both the mother and the child.
The second type of diabetes is more common and is caused by a combination of factors such as a sedentary lifestyle and obesity. Stress also plays an important role. Gestational diabetes ensues due to hormonal changes occurring during pregnancy.
Regular urination, continual thirst and hunger, extreme fatigue, and weight loss are common indications of diabetes. But that may only be present in 60% of patients. Even after looking into the symptoms, diabetes cannot be examined through blood tests alone.
The common tests for debate are the fasting plasma glucose and oral glucose tolerance tests.
Also Read: WHO visions for oral and nasal Covid-19 vaccines to take ahead to fight against Covid-19