Tumors can reduce a person’s ability to breathe, and though these tumors start in the lung cells, they can spread to other parts of the body. Lung cancers are the leading cause of death by cancer worldwide. In this post, we are gonna discuss everything you need to know about lung cancer.
Although lung cancer can affect even healthy lungs, people who smoke have the greatest risk of lung cancer. It has been seen in various studies that the risk of lung cancer increases if you have smoked for a longer duration of time and is also affected by the number of cigarettes you’ve smoked. If a person decides to quit smoking even after several years, there is still a chance to reduce the risk of developing lung cancer.
Types of Lung Cancer:
Most lung cancers start in the lining of the airway passages connecting the lungs with the outside environment. The airway passage includes the trachea and bronchi. These cancers are found in the glands that line the epithelium of bronchi and also frequently outside the lungs. The two major types of lung cancer are small-cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, each of which grows and spreads in different ways.
Non-small cell lung cancer
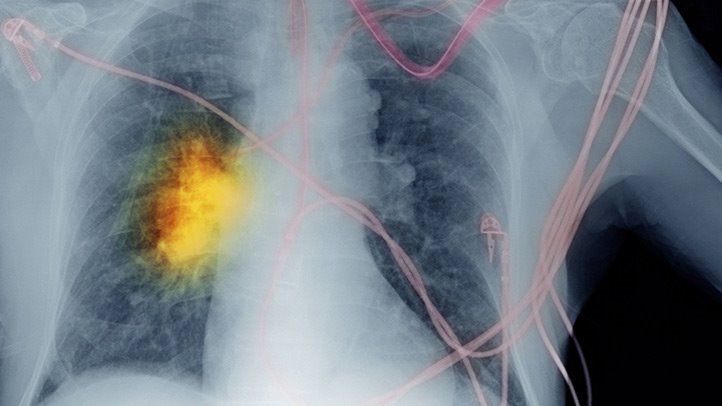
This type of lung cancer is seen in more patients than in small cell lung cancer. Moreover, nonsmall cell lung cancer also grows and spreads more slowly than small cell lung cancer. Based on the type of cell from which cancer develops, Non-small cell lung cancer is further divided into Adenocarcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Large Cell Carcinoma.
Small cell lung cancer
The small cell subtype of lung cancer is more uncommon than non-small cell cancer in the lungs representing around 15% of all cellular cancers of the lungs. This type of lung cancer develops quickly, and it is more like to spread rapidly to other parts of the body by the time a diagnosis is made.

The staging of such types of cancers also plays a pivotal role in helping healthcare professionals decide the best suitable course of treatment. Staging is done on the bases of how much the malignant tumor has spread in the body and how severe it is. Based on staging, Lung cancer can be staged as:
- Localized stage: When the cancer is within a limited area
- Regional stage: When cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes
- Distant stage: When cancer has spread to other parts of the body
Symptoms of Lung Cancer:
The patient might not complain of any symptoms during the initial stages of lung cancer. Although, early symptoms do occur in some rare cases and they can include signs such as shortness of breath, along with unexpected symptoms, such as back pain.
Other early signs of lung cancer may include:
- a lingering or worsening cough
- coughing up phlegm or blood
- chest pain that worsens when you breathe deeply, laugh, or cough
- hoarseness
- wheezing
- weakness and fatigue
- loss of appetite and weight loss
- pneumonia or similar recurrent respiratory tract infections
Treatment:
Lung cancer is one of the most challenging malignancies to treat completely. The type of cancer and the stage of progression are the most important factors when the treatment of lung cancer is determined. Most of the cases that are diagnosed at a localized stage are generally curable. Unfortunately, most people are diagnosed when the disease has spread outside the chest or involves the nodes in the chest.
In the beginning phases of non-small cell malignant cancer, chemotherapy might be utilized in association with surgical procedures to further increase the survival rates. In more developed cases of non-small cell carcinoma and in all phases of small cell lung carcinoma, chemotherapy and targeted treatments might be utilized to relieve symptoms and expand life. Chemotherapy influences both typical cells and malignant growth cells. Your treating physicians will attempt to forestall side effects as much as possible while treating cancer appropriately.
Radiation therapy is designed to maximize its effect on the cancer cells while minimizing injury to normal cells. It is a type of focused treatment option. Radiation to treat lung cancer most often comes from a machine (external radiation). Sometimes, to reduce the after-effects of radiation, tubes are used that place radioactive seeds directly in close proximity to the tumor.
The treatment of choice for early-stage lung cancer is still considered to be surgical treatment. Removing the tumor and surrounding lung tissue gives the best chance of cure for patients whose disease is localized. Here was the wrap up on everything you need to know about lung cancer.
Lung cancer still poses a gigantic threat to healthcare systems around the world. Even after treatment, patients of lung cancer are called for frequent follow ups. Follow-up in patients whose lung cancer is metastatic and/or treatment is intended to improve the quality of life and extend life.
Also Checkout: Corbevax approved by the DCGI as a COVID-19 booster for people above 18 years of age
Source: The Healthcare Daily















