It employs electromagnetic waves to recognize and track tags affixed to items automatically. A radio transponder, a radio receiver, and a transmitter make up an RFID system. The tag transmits digital data, generally, an identifying inventory number, back to the reader when activated by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device. This number can be used to keep track of your inventory.
The RFID reader’s probing radio waves provide energy to passive tags. Because active tags are battery-powered, they can be read from a wider distance from the RFID scanner, up to hundreds of meters.
RFID tags are widely employed in a variety of sectors. For example, an RFID tag applied to a vehicle during manufacture may be used to trace its progress through the assembly line, RFID-tagged medications can be tracked via warehouses, and RFID microchips implanted in cattle and pets can be used to positively identify animals.
In stores, tags can be used to speed up checkout and prevent theft by consumers and personnel. RFID tags may be affixed to tangible money, clothing, and property, as well as implanted in animals and people, raising severe privacy problems as a result of these concerns, standard standards addressing privacy and security issues have been developed.
How RFID is used in agro-tech?
Profitability and expediency are becoming more important as the world evolves. It is very difficult to keep this sector safe in India because it is an agro-based country with a wide variety of products that is influenced by a number of factors such as weather conditions and the spread of diseases or pests during agriculture production, deterioration of fresh produce during post-harvest handling, geographical distances between areas of production and areas of consumption, and so on.
Maintaining a safer food supply by coordinating product monitoring from suppliers and facilitating traceability from supplier to customer in the market is equally tough.
It’s vital to have rapid access to the most comprehensive set of data on food safety and quality concerns. Recent technical advancements in the areas of networking devices, sensors, and communication technology have a substantial impact on the agro-food sector’s long-term viability and delivering the right product to the right client at the right time.
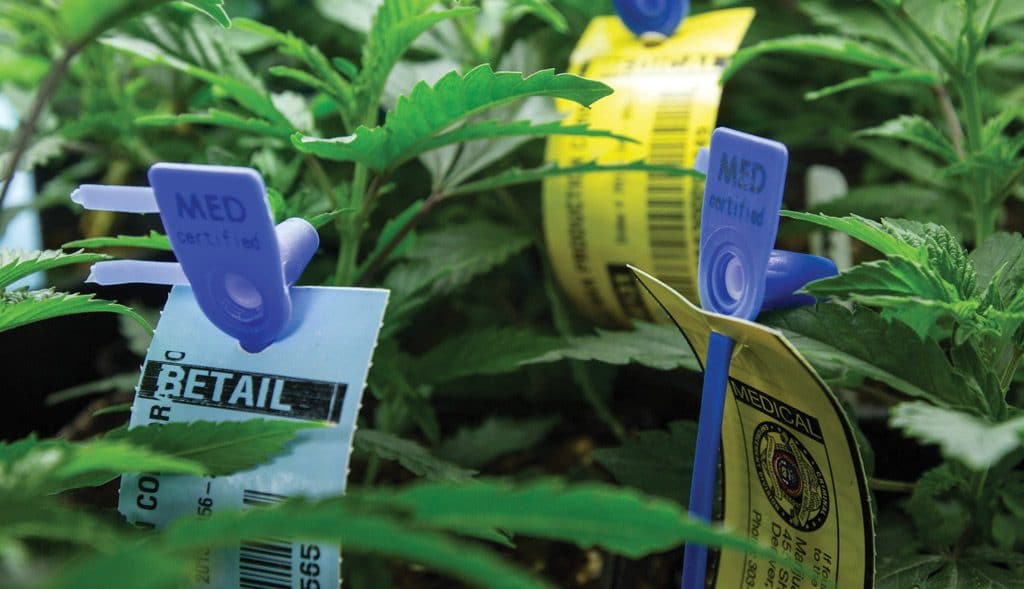

One such widespread technology is radio frequency identification (RFID), which is being used in food logistics, supply chain management, cold chain monitoring, and retail. RFID has a number of benefits over older technologies such as barcodes and data recorders.
RFID technology is more precise and does not require eye contact. It delivers real-time data that can assist retailers and distributors with product delivery schedules, as well as allowing customers to detect interior food product details along the supply chain. By providing the metric setting and tracking for particular warehouses, departments, and processes, may help increase accountability.
The earliest uses were established solely for identification; however, as interest in other prospective applications has grown, a new variety of RFID devices with sensors has been developed. The purpose of this article is to examine the many uses of RFID in the food and agricultural industry, as well as its benefits over traditional methods and future prospects in this area.
What is the role played by RFID?
RFID is the earliest era used for records recording and control of farm animals. Implanting farm animals with an RFID enhanced microchip or ear tag might now no longer most effectively permit instant identity however additionally maintain a big selection of character data including frame type, increase development, breeding lineage and lactation quality.
RFID consequently allows the recording and monitoring of character animals over their entire lifecycle. RFID utilization enables to reveal fitness of the herd, maintain character medicinal drug and vaccination records, and prevent the unfold of sickness with the aid of using monitoring and segregating infected farm animals at early stages, main to hit isolation and remedy that saves the relaxation of the herd and keep the quality of respective animal meat.
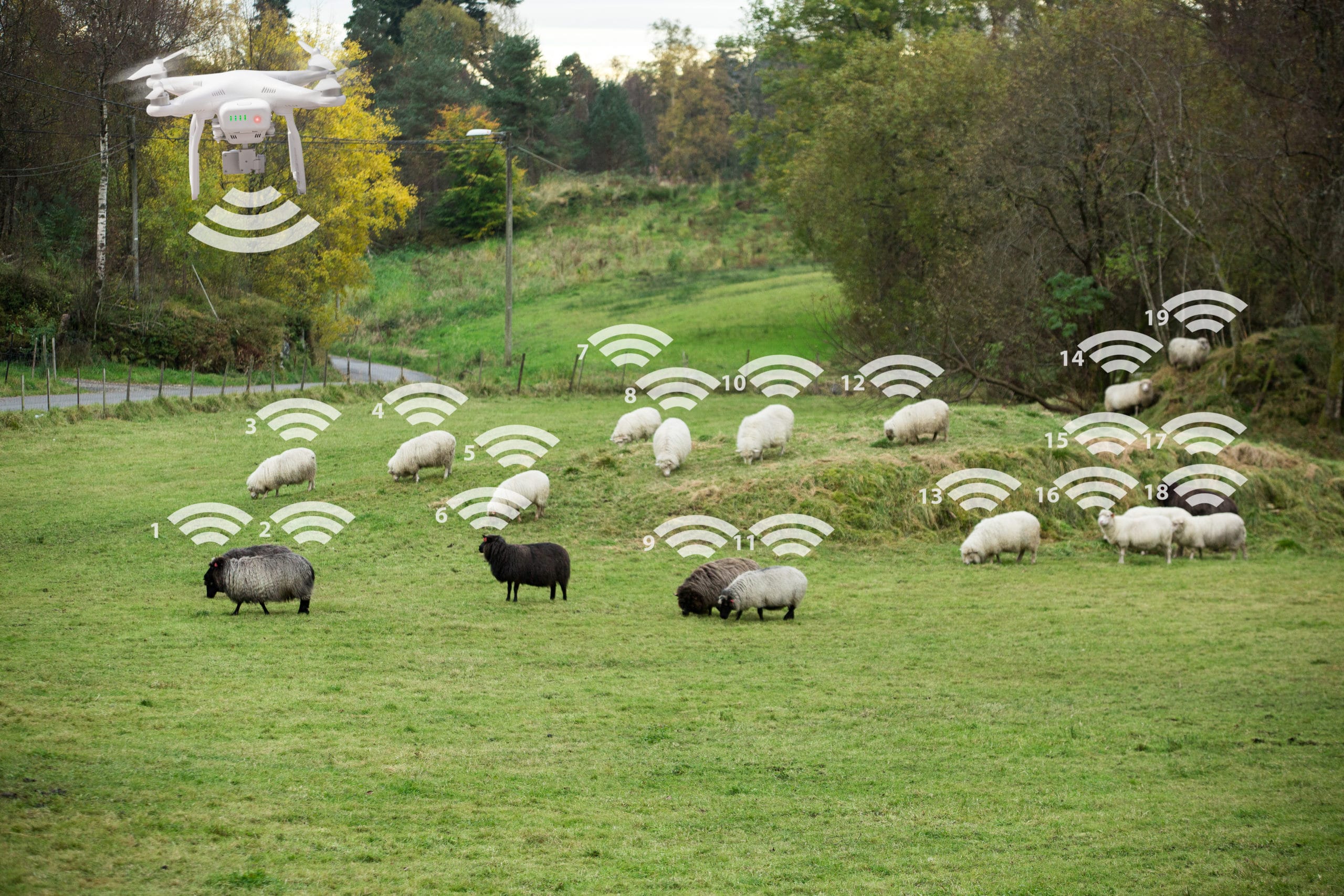

RFID tag facts consist of humidity, light, wind, pace and rainfall all through plantation and cultivation. By placing RFID tags into collar, card, injection, tablet or simply on agricultural products’ programs and deciding the healthful situation of the product.
It is handy for processing businesses to concurrently upload facts at the tag, consisting of business code, processing date, processing batch, and package deal weight, etc. utilized in processing. Therefore, the continuity of agricultural product facts may be efficiently stored along with the delivery chain.
RFID may be used for plant fitness control, in particular for planet fitness inspection and certification, agrochemical control, and their effect assessment. Radiofrequency identity ought to assist to lessen the unfolding of plant pathogens. RFID has been inserted in lots of flowers for distinct functions like in Cactus to keep away from the theft, Citrus tree for tracking ailment and breeding, Cypress for ailment tracking and grapevine for traceability and the clonal selection and in roses for virtual city garden control.
What are the benefits of RFID?
Advantages of RFID in fewer manufacturing processes Manual labor, less cost, better visibility, and planning. of Warehouse process, it provides accurate real-time insights Information, quick location of products, recording options Ability to strategically plan losses, product locations. RFID input Container management and tracking provide real-time transparency Cargo movement improves efficiency and accuracy. So Sales process, accelerated delivery, improved efficiency, Increase accuracy, and reduced distribution cost.
Together with the corresponding RFID generation infrastructure, it enables traceability from stops in the distribution chain at a very low cost. The implementation of RFID helps manufacturing manufacturers overcome the problem of corruption.
Using RFID It is completely possible to control training temperatures and shelves with perishable devices at all levels of the load-free chain. Allows all manufacturers and customers to notify the status of the storage release. Competitive pressures, regulatory requirements, global supply chains and protection issues in the agribusiness sector are overcome with the RFID generation.
In addition to its Services, certain difficult situations and obstacles also come with it which we face this generation and in the years to come. RFID works in harsh dust and extreme environments Long-term temperature Facts that are difficult to operate and I’ve wanted to read for a long time Frequency level due to reduced code strength Operation at different frequencies different standards Level of particle size.
However, in the previous study Hope to expand some applications in order to be able to convert the collected facts into useful information with the help of a unique algorithm. RFID use is booming within the next few years as a result of product and other benefits. Safer with low-cost identification and logistics tracking. Revolutionizing agricultural logistics will be the economic growth of the newborn.
Also Read: Pearl Farming; An Emerging Asset For Farmers
Source: TheAgrotechDaily
















